giáo khi em kết thúc lệnh offset máy cứ báo lỗi không được CỤ THỂ KHI
Chào thầy giáo khi em kết thúc lệnh offset máy cứ báo lỗi không được. CỤ THỂ KHI EM BẤM HỖ TRỢ THÌ NỘI DUNG NHƯ SAU Ạ:
Formulas can sometimes result in error values in addition to returning
unintended results. This article summarizes some of the most common errors that
a user can make when entering a formula, and explains how to correct those
errors.
![]() Make sure it's constructed correctly
Make sure it's constructed correctly
![]() Start every function with the equal sign
Start every function with the equal sign
=()
![]() Match all opening and closing parentheses
Match all opening and closing parentheses
![]() Enter the correct type of arguments
Enter the correct type of arguments
![]() Nest no more than 64 functions
Nest no more than 64 functions
![]() Enclose other sheet names in single quotation
Enclose other sheet names in single quotation
marks
![]() Place an exclamation point (!) after a worksheet
Place an exclamation point (!) after a worksheet
name when you refer to it in a formula
![]() Include the path to external workbooks
Include the path to external workbooks
![]() Find something outside of the formula that was
Find something outside of the formula that was
deleted or renamed
![]() Avoid using numbers with decimal separators in
Avoid using numbers with decimal separators in
formula arguments
Make sure it's constructed correctly
Start every function with the equal sign (=)
If you omit the equal sign, what you type may be displayed as text or as a
date. For example, if you type SUM(A1:A10), Excel displays
the text string SUM(A1:A10) and does not calculate the
formula. If you type 11/2, Excel displays a date, such as
2-Nov or 11/02/2009, instead of dividing 11 by 2.
Match all opening and closing parentheses
Make sure that all parentheses are part of a matching pair. When you use a
function in a formula, it is important for each parenthesis to be in its correct
position for the function to work correctly. For example, the formula =IF(B5<0),"Not valid",B5*1.05) will not work because there
are two closing and only one opening parenthesis. The correct formula looks like
this: =IF(B5<0,"Not valid",B5*1.05).
Enter all required arguments
Some worksheet functions have required arguments (argument: The values that a function uses to perform
operations or calculations. The type of argument a function uses is specific to
the function. Common arguments that are used within functions include numbers,
text, cell references, and names.), and some functions (such
as PI) take no arguments. Also, make sure that you have not
entered too many arguments. For example, the UPPER function
accepts only one string of text as its argument.
Enter the correct type of arguments
Some worksheet functions, such as SUM, require numerical
arguments. Other functions, such as REPLACE, require a text
value for at least one of their arguments. If you use the wrong type of data as
an argument, Excel might return unexpected results or display an error.
Nest no more than 64 functions
You can enter, or nest, up to 64 levels of functions within a function. For
example, the formula =IF(SQRT(PI())<2,"Less than two!","More
than two!") contains three functions: The PI function is
nested inside the SQRT function, which is in turn nested
inside the IF function.
Enclose other sheet names in single quotation
marks
If the formula refers to values or cells on other worksheets or workbooks,
and the name of the other workbook or worksheet contains a non-alphabetical
character (such as a space), you must enclose its name within single quotation
marks ( ' ).
Place an exclamation point (!) after a worksheet name when
you refer to it in a formula
For example, to return the value from cell D3 in a worksheet named Quarterly
Data in the same workbook, use this formula: ='Quarterly
Data'!D3.
Include the path to external workbooks
Make sure that each external
reference (external
reference: A reference to a cell or range on a sheet in another Excel workbook,
or a reference to a defined name in another workbook.)
contains a workbook name and the path to the workbook.
A reference to a workbook includes the name of the workbook and must be
enclosed in brackets ([]). The reference must also contain
the name of the worksheet in the workbook.
For example, to include a reference to cells A1 through A8 on the worksheet
named Sales in the workbook (that is currently open in Excel) named Q2
Operations.xlsx, the formula looks like this: =[Q2
Operations.xlsx]Sales!A1:A8.
If the workbook that you want to refer to is not open in Excel, you can still
include a reference to it in a formula. You provide the full path to the file,
such as in the following example: =ROWS('C:\My Documents\[Q2
Operations.xlsx]Sales'!A1:A8). This formula returns the number of rows in
the range that includes cells A1 through A8 in the other workbook (8).
Note If the full path contains space characters, as
does the preceding example, you must enclose the path in single quotation marks
(at the beginning of the path and after the name of the worksheet, before the
exclamation point).
Avoid dividing by zero
Dividing a cell by another cell that either contains zero or no value can
result in a #DIV/0! error.
For more information about this error, see Correct a
#DIV/0! error.
Find something outside of the formula that was deleted or renamed
A column of data was deleted
If you delete a column in a worksheet range or in an Excel table, a formula
that depends on that column might return a #REF! error. To fix this, select any
cell that contains the #REF! error and press F2 to edit the formula. In the
formula bar, select #REF! and delete it. Then, reenter the range for the
formula. Doing this should fix all the broken formulas in that column.
For more information about this error, see Correct a
#REF! error.
A defined name was deleted
If you delete a defined name, a formula that depends on that defined name
returns a #NAME? error. To fix this, either define a new name that refers to the
range that you want, or change the formula to refer directly to the range of
cells (for example, A2:D8).
For more information about this error, see Correct a
#NAME? error.
A worksheet was deleted
If you delete a worksheet, a formula that depends on the worksheet returns a
#REF! error. There is no way to fix this — a worksheet that you've deleted can't
be recovered.
For more information about this error, see Correct a
#REF! error.
A workbook was deleted
If you delete a workbook, the values in any cells that refer to that workbook
remain intact until you update the formula.
For example, if your formula is =[Book1.xlsx]Sheet1'!A1
and you delete the file Book1.xlsx, the values referenced from that workbook
remain intact. If you edit and then try to save a formula that refers to that
workbook, Excel displays the Update Values dialog box and
prompts you to enter a file name. If you click Cancel, the data
in your cell stays unchanged. To make sure that this data is not lost, convert
the cells containing references to a deleted workbook from a formula to a value
by copying the cell and then using the Paste command to paste
the value into the cell.
Avoid using numbers with decimal separators in formula arguments
Enter numbers without decimal separators
Do not enter numbers with decimal separators when you enter them in formulas,
because commas are used as argument separators in formulas. For example, if the
value that you want to enter is $1,000, enter 1000 in the
formula. If you enter a comma as part of a number, Excel interprets the comma as
a character that separates values into separate formula arguments. If you want
the numbers of the formula results displayed so that they show thousands or
millions separators, or currency symbols, format the cells after you
enter the formulas that use unformatted number arguments.
For example, if you want to add 3100 to the value in cell A3, and you enter
the formula =SUM(3,100,A3), Excel adds the numbers 3 and 100
and then adds that total to the value from A3, instead of adding 3100 to A3.
Or, if you enter the formula =ABS(-2,134) to find the
absolute value of -2134, Excel displays an error because the ABS function accepts only one argument — Excel sees the comma
and interprets the formula like this: "find the absolute value of -2 and 134."
Because the ABS function can operate on only one number,
Excel displays an error message.

Chào bạn, bạn vui lòng chụp lỗi lên giúp gitiho nhé.
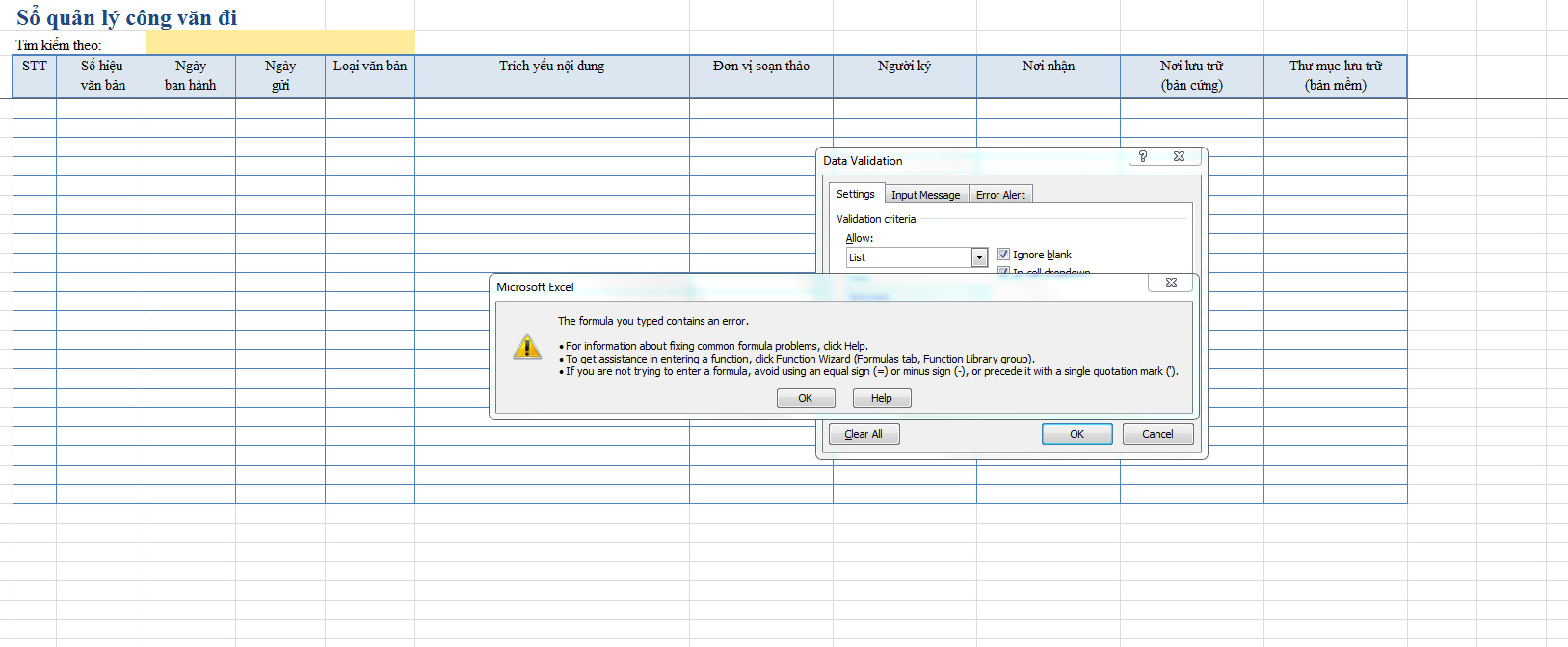

Bạn xem lại việc sử dụng dấu ngăn cách các thành phần trong hàm và đóng ngoặc cho đúng các vị trí nhé. Ở đây thông báo lỗi là bạn viết chưa đúng cú pháp thôi, không phải là không làm được. Bạn có thể viết công thức đúng như hướng dẫn ra bên ngoài trước, sau đó copy và dán vào vùng đặt tên này.

Chào bạn nếu bạn chưa viết quen thì nên viết ra cells rồi copy vào nhé, và xem kỹ dấu phân cách , hoặc ; nhé.
Câu hỏi liên quan
Giấy chứng nhận Đăng ký doanh nghiệp số: 0109077145, cấp bởi Sở Kế hoạch và Đầu tư TP. Hà Nội
Giấy phép mạng xã hội số: 588, cấp bởi Bộ Thông tin và Truyền thông